

12.12 2023
SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE 26 Jul 2023 Vol 15, Issue 706 DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adg3358
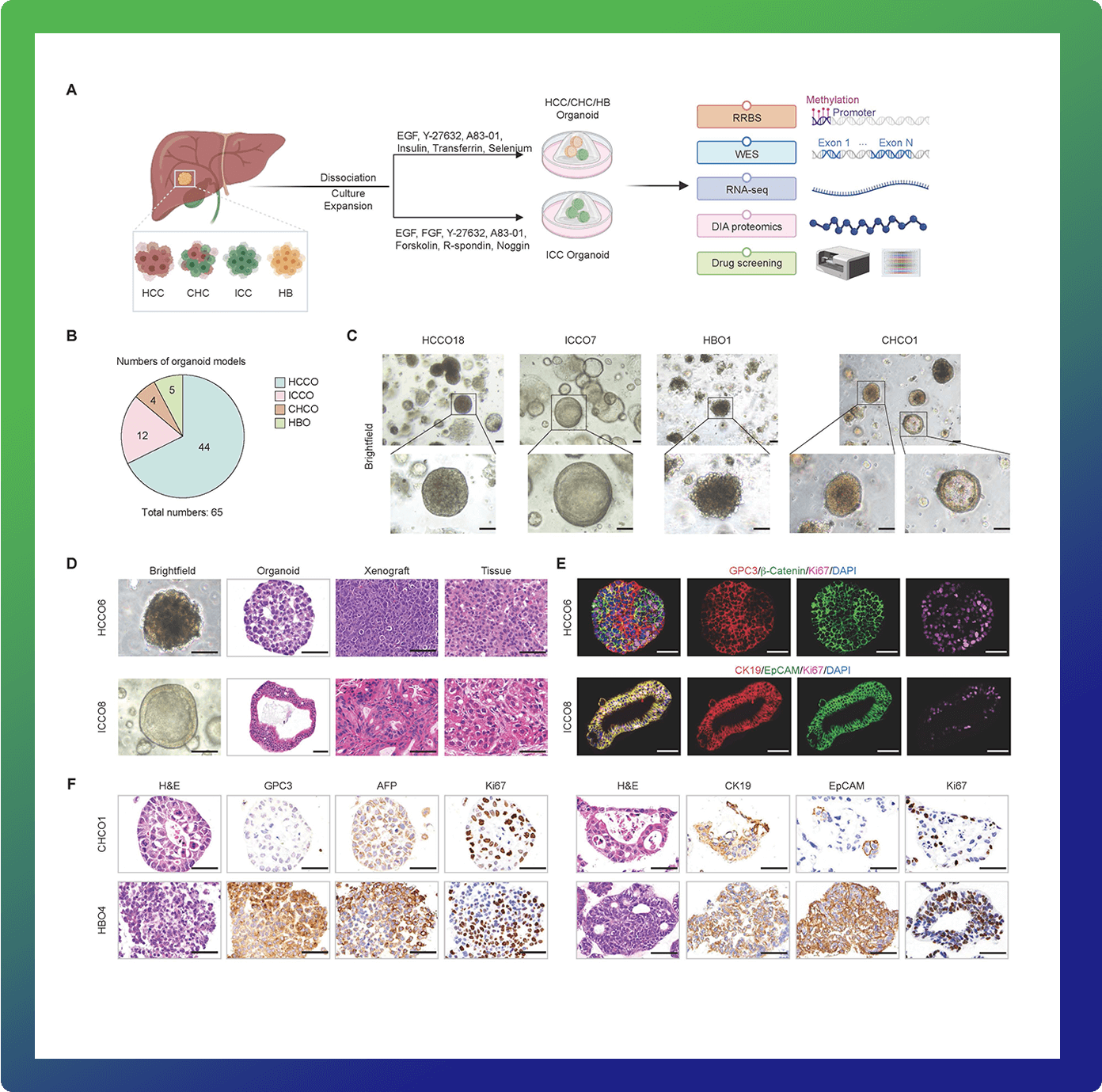
Organoid models have the potential to recapitulate the biological and pharmacotypic features of parental tumors. Nevertheless, integrative pharmaco-proteogenomics analysis for drug response features and biomarker investigation for precision therapy of patients with liver cancer are still lacking.We established a patient-derived liver cancer organoid biobank (LICOB) that comprehensively represents the histological and molecular characteristics of various liver cancer types as determined by multiomics profiling, including genomic, epigenomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic analysis. Proteogenomic profiling of LICOB identified proliferative and metabolic organoid subtypes linked to patient prognosis. High-throughput drug screening revealed distinct response patterns of each subtype that were associated with specific multiomics signatures. Through integrative analyses of LICOB pharmaco-proteogenomics data, we identified the molecular features associated with drug responses and predicted potential drug combinations for personalized patient treatment. The synergistic inhibition effect of mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus and the multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor lenvatinib was validated in organoids and patient-derived xenografts models. We also provide a user-friendly web portal to help serve the biomedical research community. Our study is a rich resource for investigation of liver cancer biology and pharmacological dependencies and may help enable functional precision medicine.
本研究对65 个肝癌患者来源类器官(PDO)模型进行了全面的药物蛋白基因组学分析,基于蛋白质组学的特征建模重现了肝癌组织的蛋白基因组学分子分型,实现药物反应的高精准预测并评估了潜在的药物联合治疗方案,为临床患者选择和药物联合治疗提供指导。
原文链接https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.adg3358


